Sinensetin
Sinensetin
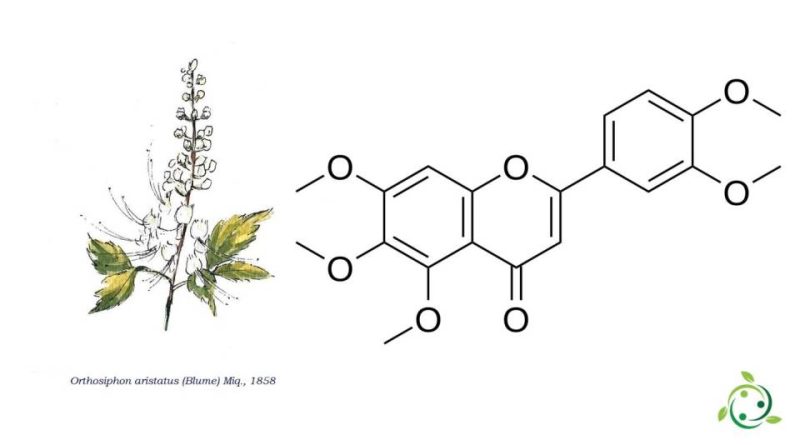
Sinensetin, whose term in the official IUPAC nomenclature is: 2- (3,4-dimethoxyphenyl) -5,6,7-trimethoxychromene-4-one, is a methylated flavone with a brute or molecular formula: C20H20O7.
Sinensetin is a natural substance found in Java tea (Orthosiphon aristatus (Blume) Miq.) And orange oil.
Sinensetin, also known as: 5,6,7,3 ‘, 4’-pentamethoxiflavone is a methylated flavone similar to the natural flavones apigenin, luteolin and the synthetic flavones diosmin and flavoxate.
The presence, in position C3, of a methyl confers to this substance remarkable antiangiogenic properties; compared to a lower toxicity due to the lack of the methyl group in the C8 position.
The alcoholic extracts of Orthosiphon aristatus, which contain sinensetin, have two enzymes: α-glucosidase and α-amylase which give the extract antidiabetic properties in non-insulin-dependent diabetes.
Sinensetin also boasts anti-inflammatory and antipyretic properties.
Sinensetin also has the ability to prevent and / or improve the treatment of obesity, through a property of downregulation of the metabolic pathway mediated by SREBP1c (Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Protein that influence DNA transcription) and, moreover, it increases the phosphorylation of protein kinase A and hormone-sensitive lipase, indicating lipolytic properties for sinensetin via a cAMP-mediated metabolic signaling pathway.
Another property at the center of studies and laboratory research is that of reducing the signaling mechanisms of bacterial cells and their adhesiveness (quorum sensing).
In addition, some in vitro research has shown antimutagenic properties for sinensetin, which would suggest chemo preventive characteristics, in the absence of genotoxic properties.
Finally, a 2002 study is interesting in which sinensetin demonstrated chemosensitizing properties to anticancer drugs, with the advantage also of having a high therapeutic index, of being a non-transportable inhibitor, and of not inducing P-glycoprotein.
Warning: The information shown is not medical advice and may not be accurate. The contents are for illustrative purposes only and do not replace medical advice.