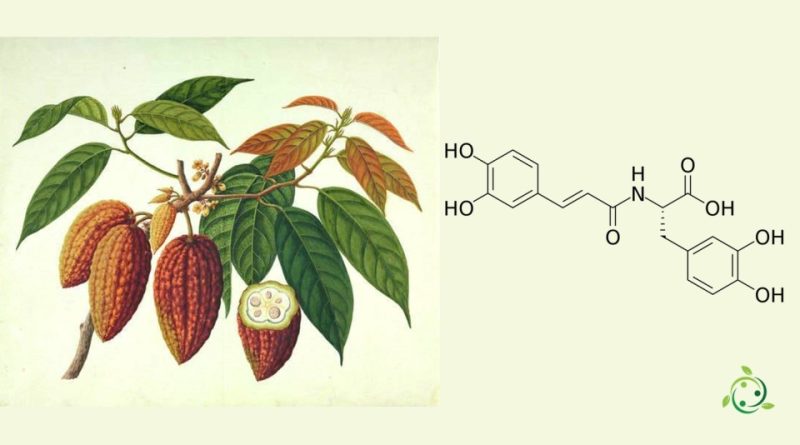
Clovamide
Clovamide
Clovamide, whose term in the official IUPAC nomenclature is: 3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2S-[[3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2Z-enoyl]amino]propanoic acid is a polyphenol found in the cocoa mass.
Clovamide has a brute or molecular formula: C18H17NO7.
The concentration of this substance in cocoa (Theobroma cacao L., 1753) varies with the geographical origin and decreases considerably with roasting.
In the laboratory, clovamide can be synthesized from L-phenylalanine and caffeic acid.
Clovamide belongs to a group of oxidizing substances found in cocoa.
The abundant presence of these antioxidant substances in cocoa, in particular of polyphenols (catechins and anthocyanins) and flavonoids which, as we now know, contribute to defending the entire body from the attack of free radicals and therefore have an anti-aging effect.
Among these substances, with a very strong antioxidant action, we find clovamide, whose activity is even comparable to that of vitamin C.
In general, this polyphenol is the most antioxidant substance present in cocoa derivatives.
Warning: The information provided is not medical advice and may not be accurate. The contents are for illustrative purposes only and do not replace medical advice.