Azelaic acid
Azelaic acid
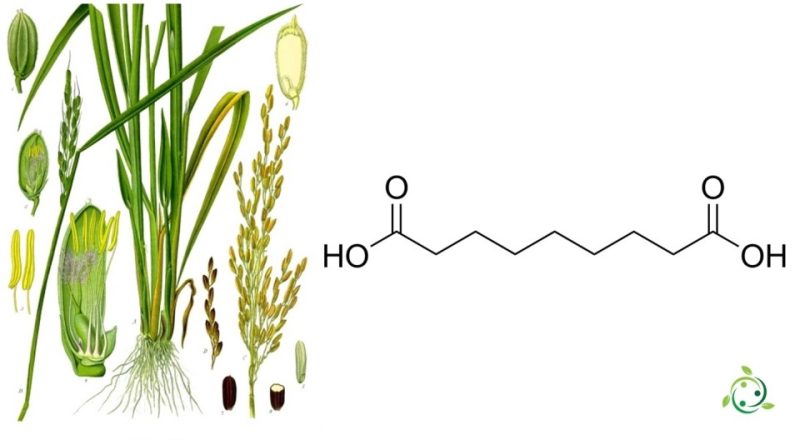
Azelaic acid, whose term in the official IUPAC nomenclature is: Nonanedioic acid, is a dicarboxylic acid with the brute or molecular formula: C9H16O4.
Azelaic acid is a straight-chain saturated dicarboxylic acid. Its structure contains two carboxyl groups (-COOH) and an aliphatic chain of nine carbon atoms. Azelaic acid is a white, crystalline compound at room temperature, and is soluble in water and organic solvents.
This molecule is a natural substance produced by Malassezia furfur which is a yeast found on normal skin. It occurs naturally in wheat, rye and barley.
Azelaic acid is known for its beneficial properties on the skin and is used in various cosmetic and pharmaceutical products. Some of its main uses include:
– Treatment of acne: Azelaic acid is an antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory agent that helps reduce the number of bacteria that cause acne and prevent the formation of comedones.
– Treatment of rosacea: Azelaic acid can reduce the redness and inflammation associated with rosacea, a skin condition characterized by redness and pustules.
– Skin Brightening: Azelaic acid can help reduce dark spots and hyperpigmentation on the skin, thereby improving skin tone and appearance.
– Treatment of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation: Can be used to reduce dark spots left by acne, burns or other skin lesions.
– Inhibition of hair growth: Azelaic acid can be used to reduce the growth and diameter of unwanted hair.
Azelaic acid is usually applied topically to the skin in the form of a cream, gel or lotion. It is generally well tolerated and has few side effects, but it is always best to follow your doctor’s or manufacturer’s directions for proper use.
Azelaic acid inhibits 90% of the enzyme 5-alpha H-reductase, involved in the synthesis of androgens.
This compound is also:
– Antibacterial: reduces the growth of bacteria in the follicle (Propionibacterium acnes and Staphylococcus epidermidis);
– Keratolytic and comedolytic: normalizes the abnormal growth of the cells of the epidermis, which line the follicle;
– Fights free radicals and reduces inflammation;
– Reduces pigmentation: it is particularly effective for patients with very dark skin, suffering from melasma, or for freckles left by acne.
– It is non-toxic and is well tolerated by most of the patients treated.
Remember, however, that since a 20% solution of azelaic acid can be irritating to the skin, its use must be linked to a doctor’s prescription.
Warning: The information provided is not medical advice and may not be accurate. The contents are for illustrative purposes only and do not replace medical advice.