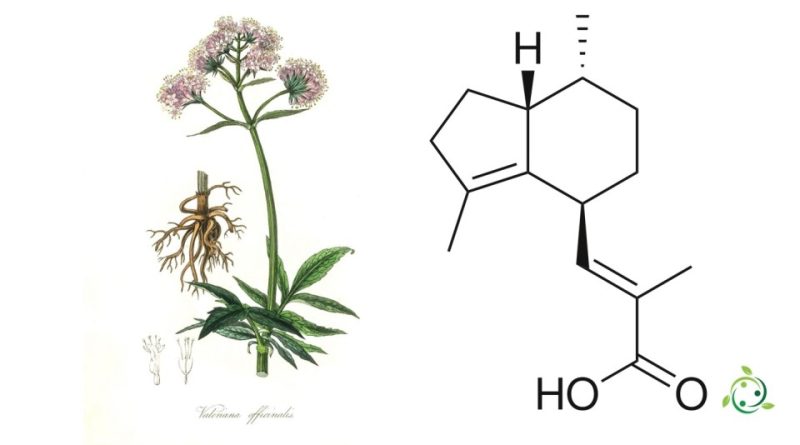
Valerenic acid
Valerenic acid
Valerenic acid, whose term in the official IUPAC nomenclature is: 3-[3,7-dimethyl-2,4S,5,6,7R,7aR-hexahydro-1H-inden-4-yl]-2-methylprop acid -2E-enoic is a sesquiterpenoid with a brute or molecular formula: C15H22O2.
Valerenic acid is present in valerian essential oil and is thought to be one of the compounds responsible for the sedative effect of valerian.
Valerenic acid is, therefore, a chemical compound present in nature and, more precisely, in the roots of various plants of the genus Valeriana, including Valeriana officinalis. Valerian is a plant known for its sedative and anti-anxiety properties and has traditionally been used as a herbal remedy to relieve insomnia, anxiety and stress.
Valerenic acid is considered to be one of the major active compounds in valerian and has been studied for its impact on the central nervous system. It is believed to have calming and relaxing effects on the brain, which can help reduce nervous excitability and promote sleep.
However, it’s important to note that research on valerian and its constituents, including valerenic acid, is not conclusive in all cases. While some studies suggest benefits for insomnia and anxiety, others report mixed results. Also, as with any supplement or medication, there may be side effects or interactions with other medications, so it is advisable to consult a health care professional before use.
Valerenic acid acts as a positive allosteric modulator of the subtype selective GABAA receptor via a binding site in the transmembrane domain at the β+α- interface. In receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes (frog eggs) it was shown that only ensembles incorporating β2 or β3 subunits were stimulated by valerenic acid. A study in mice has shown that a single amino acid substitution (N265M) in the β3 subunit severely reduces the anxiolytic effect. Modulation of ion channel action was not significantly dependent on incorporation of α1, α2, α3 or α5 subunits.
At the 5-HT5A receptor valerenic acid acts as a partial agonist. This serotonin receptor subtype is distributed in the suprachiasmatic nucleus, a tiny brain region involved in the sleep-wake cycle.
A 2006 study found that valerian extract and valerenic acid inhibit NF-κB, a protein complex that controls DNA transcription, in HeLa cells (cultured human cancer). This was measured with the IL-6/Luc (interleukin-6 luciferase) assay as a measuring tool. The study stated that such inhibition may be linked to the valerian plant’s reported anti-inflammatory action.
Warning: The information provided is not medical advice and may not be accurate. The contents are for illustrative purposes only and do not replace medical advice.