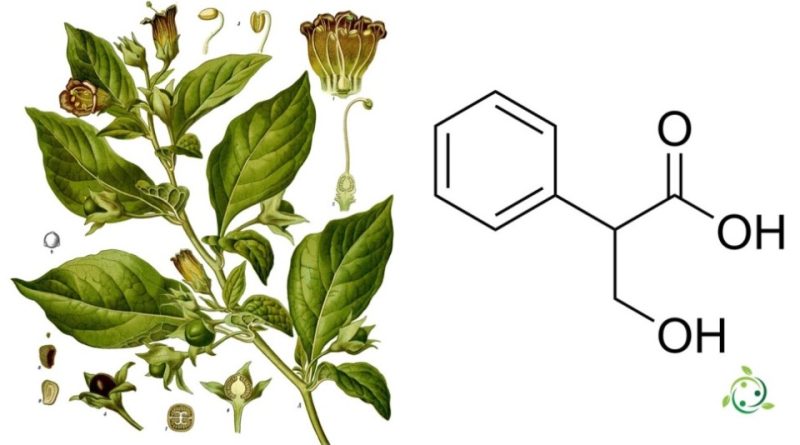
Tropic acid
Tropic acid
Tropic acid, whose term in the official IUPAC nomenclature is: (RS) 2-phenyl-3-hydroxypropanoic acid, is an organic compound that belongs to the class of carboxylic acids. It has several characteristics that make it interesting from a chemical and biological point of view.
Here are some of its main features:
– Molecular structure: Tropic acid has a chemical formula C9H10O3 and has a main carbon chain of three carbon atoms, with a carboxyl group (-COOH) at the end and a phenyl group (-C6H5) attached to the carbon atom central.
– Solubility: Tropic acid is soluble in polar solvents such as water, alcohol and diethyl ether.
– Acidic properties: As the name suggests, tropic acid is a carboxylic acid and has a carboxyl group that gives it acidic properties. It can donate a proton (H+ ion) in aqueous solution and then react with bases to form salts.
– Biological activity: Tropic acid has been studied for its potential biological properties. It has been identified as a possible anticancer agent, with potential cytotoxic effects on cancer cells.
– Chemical synthesis: Tropic acid can be synthesized through various chemical routes, for example from phenylacetone via a Friedel-Crafts reaction followed by a hydrolysis reaction.
Tropic acid is present in various plants, but its concentration varies from species to species. Some of the plants where tropic acid can be found include:
– Atropa belladonna: commonly known as nightshade or deadly nightshade, it is a poisonous plant that contains tropic acid in its roots and leaves.
– Datura spp.: plants of the genus Datura, such as Datura stramonium or Datura metel, contain tropic acid in their aerial parts, including flowers, leaves and seeds.
– Brugmansia spp.: also known as angel’s trumpet, the genus Brugmansia includes ornamental plants that contain tropic acid in their plant tissue.
– Hyoscyamus niger: known as witchcraft bean or black St. John’s wort, this plant contains tropic acid in several parts, including seeds, leaves and flowers.
– Mandragora spp.: the genus Mandragora includes several species of plants that contain tropic acid in their roots, such as Mandragora officinarum.
Importantly, many of these plants are extremely toxic and should be handled with caution. The use of these plants for medicinal or therapeutic purposes requires adequate knowledge and supervision by experienced professionals.
Warning: The information provided is not medical advice and may not be accurate. The contents are for illustrative purposes only and do not replace medical advice.