kainic acid
kainic acid
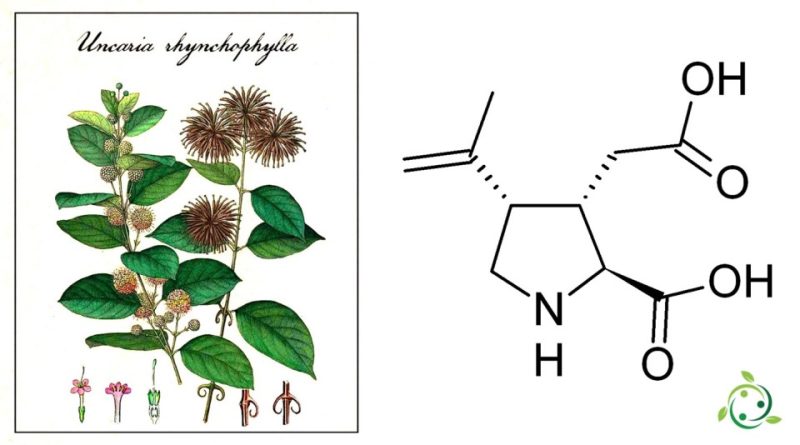
Kainic acid, whose term in the official IUPAC nomeclature is: (2S,3S,4S)-3-(carboxymethyl)-4-prop-1-en-2-ylpyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid, is a chemical compound which belongs to the family of excitatory amino acids and is found naturally in some plants, in particular in marine algae of the genus Digenea and also in Uncaria rhynchophylla.
The chemical formula of kainic acid is C10H15NO4 and was first isolated from the marine plant Kainomyces, but it can also be produced synthetically.
Kainic acid is a substance known for its ability to act as a selective agonist of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-type glutamate receptors in the brain.
In particular kainic acid is a powerful agonist of the third type of glutamate receptor known as “kainate receptor” permeable to Na+ and K+ cations. Permeability to Ca2+ is usually very slight but varies according to the subunits that make up the receptor.
The kainate receptor is tetrameric and has 4 transmembrane domains, of which the second, with a “hairpin” structure, forms the channel by juxtaposing with three others.
Kainic acid is widely used in scientific and experimental research to study glutamate receptors and their effects on the central nervous system. When administered to laboratory animals, it can induce seizures and neuronal lesions similar to those seen in epilepsy and Alzheimer’s disease.
Kainic acid is used in research to study neurodegeneration and neurological diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and stroke. Its ability to induce neuronal injury may provide insight into cell death pathways and neuronal degeneration.
However, it is important to note that kainic acid is extremely toxic and is not used in clinical or therapeutic applications in humans due to its neurotoxic effects. Its use is mainly limited to the field of scientific research and neuropharmacology. Handling and manipulation of kainic acid should be done with caution and following the appropriate safety rules.
Warning: The information provided is not medical advice and may not be accurate. The contents are for illustrative purposes only and do not replace medical advice.