Lobeline
Lobeline
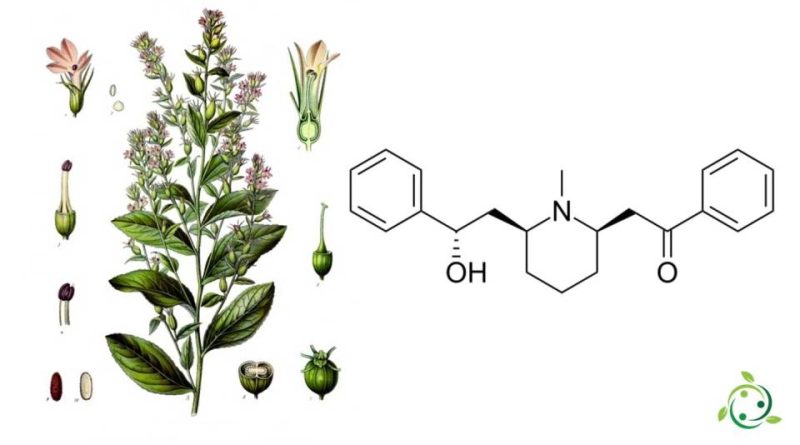
Lobeline, whose term in the official IUPAC nomenclature is: 2 – ((2R, 6S) -6 – ((S) -2-Hydroxy-2-phenylethyl) -1-methylpiperidin-2-yl) -1-phenylethanone is a pyridine alkaloid.
Lobeline has a brute or molecular formula: C22H27NO2 and is present in some plants, especially of the Lobelia genus, including Lobelia inflata, Lobelia tupa, Lobelia siphilitica, Lobelia chinensis and Hippobroma longiflora.
From the physical point of view, lobeline is presented in the form of needle-like, colorless crystals, with the property of electively exciting the respiratory center.
Lobeline is used parenterally against asphyxia in newborns, in cases of apnea or dyspnea due to nerve injuries, and intoxications from drugs with a depressive action on bulbar centers (morphine, hypnotics).
From a pharmacological point of view, lobeline has been shown to have multiple mechanisms of action, acting as a VMAT2 ligand, which stimulates the release of dopamine to a moderate extent when administered alone, but reduces the release of dopamine caused by methamphetamine.
It also inhibits the reuptake of dopamine and serotonin, and acts as a mixed agonist-antagonist to the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors to which it binds to the interfaces of the subunits of the extracellular domain.
It is also a μ-opioid receptor antagonist. It appears to be a P-glycoprotein inhibitor, according to at least one study. Inhibition of P-glycoprotein has been hypothesized to reduce chemotherapy resistance in cancer, presumably by affecting any P-gp substrate.
On the market, lobeline is found in the form of tablets, to be used as an aid to quit smoking, although research to this effect has not confirmed this property.
Furthermore, lobeline has also been studied for the treatment of other drug addictions such as addiction to amphetamines, cocaine, or alcohol; however, clinical trials have shown limited efficacy.
Among the contraindications and toxicity of lobeline it should be remembered that ingestion of this substance can cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, cough, dizziness, visual disturbances, hearing disturbances, mental confusion, weakness, slow heart rate, increased blood pressure. , increased respiratory rate, tremors and convulsions.
Furthermore, it is emphasized that lobeline has a narrow therapeutic index as the potentially beneficial dose of this substance is very close to the toxic dose.
Warning: The information shown is not medical advice and may not be accurate. The contents are for illustrative purposes only and do not replace medical advice.