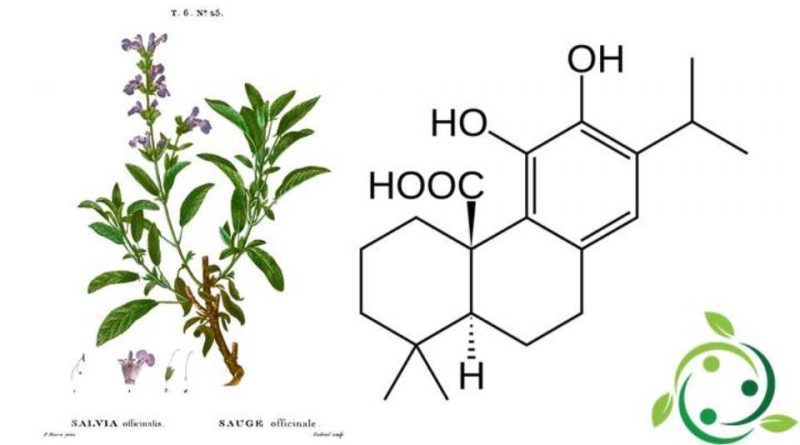
Carnosic acid
Carnosic acid
Carnosic acid whose term in the IUPAC official nomenclature is: (4a R, 10a S) -5,6-Dihydroxy-1,1-dimethyl-7-propan-2-il-2,3,4,9,10 , 10a-hexahydrofenantenene-4a-carboxylic is a natural diterpenoid present in rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L., 1753) and in common sage (Salvia officinalis L., 1753).
This acid of natural origin has a brute or molecular formula: C20H28O4 and is also known by the name of salvine.
Dried rosemary or sage leaves contain on average carnosic acid from 1.5 to 2.5%.
Carnosic acid is used as a preservative or antioxidant in food and non-food products (e.g. toothpaste, mouthwash and chewing gum, in which it has an antimicrobial effect on the microbes responsible for halitosis or skin care products).
In recent years, carnosic acid has been the subject of numerous researches, by virtue of its marked metabolic and potentially slimming activities.
For this reason, several companies in the phytotherapeutic and pharmaceutical sector have tried to develop biosynthetic techniques, capable of optimizing the synthesis of this active principle also starting from inactive metabolites.
At present, the literature on the subject is still experimental and clinically irrelevant; the use of carnosic acid would seem useful in:
– Exercise a chemo-protective and antioxidant action;
– Protect the liver from damage induced by a high fat diet;
– Contribute to neuro protection;
– Facilitate slimming;
– Modulate inflammatory processes also of a systemic nature.
Warning: The information shown is not medical advice and may not be accurate. The contents are for illustrative purposes only and do not replace medical advice.