The Escin
The Escin
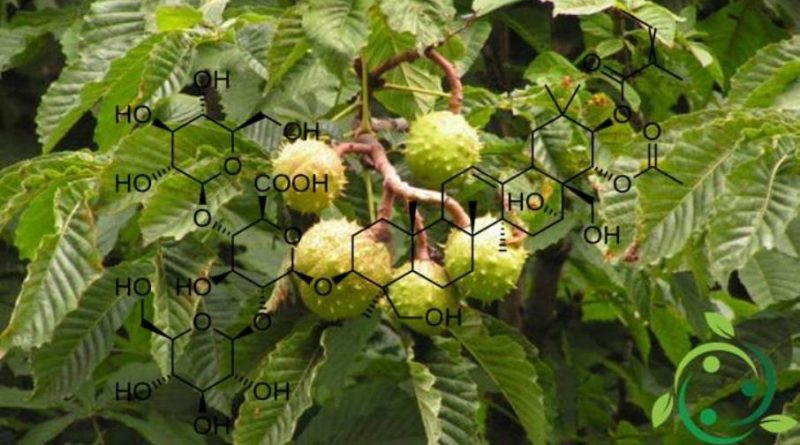
The Escin, whose brute or molecular formula is: C55H86O24, is a vegetable compound obtained from the mixture of saponins contained in the seeds, bark and leaves of the horse-chestnut (Aesculus hippocastanum L., 1753). Chemically, escin is a mixture of saponins, which are substances with anti-inflammatory, vasoprotective and vasoconstrictive properties. Once extracted from the horse chestnut tree it is subsequently purified to be suitable for oral and intravenous use.
The escin, substance, also contained in some medicinal preparations, is able to increase the resistance and decrease the permeability of the capillaries (anti-edema action): for this characteristic it is used in the treatment of various types of edemas, in case of varicose veins and hemorrhoids, hematomas and bruises and capillary fragility. For this reason, the intake of products based on escin can help the process of decreased swelling and heaviness in the lower limbs. Because it is able to increase the tonicity of the blood vessel walls and promote the contractility of the veins, reducing the stagnation of blood in the lower limbs and facilitating the return of blood to the heart, this substance can also be taken in cases of peripheral venous insufficiency.
Experimental studies have shown that the escine does not cause harmful effects on the intravenous venous or gastric mucosa. The compound is devoid of teratogenic or embryotoxic effects.
The activity of escin seems to be mainly aimed at inducing the synthesis of endothelial nitric oxide, making endothelial cells more permeable to calcium, also inducing the release of prostaglandin F2α.
Escin is contraindicated in subjects that show known hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients used in the pharmaceutical form. It is also contraindicated in subjects with renal insufficiency, previous hemolytic disorders, generalized edema of cardiac or renal origin.
With trance-based treatments, some disorders of the gastrointestinal tract (dyspepsia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, malaise and abdominal pain) and of the nervous system (headache and vertigo) have been reported. There have also been skin disorders and hypersensitivity reactions (pruritus, skin rash, dermatitis and eczema, erythema multiforme, severe allergic reactions sometimes associated with arterial hypotension and laryngeal edema).
Warning: The information reported is not medical advice and may not be accurate. The contents are for illustrative purposes only and do not replace medical advice.