Avena sativa
Avena sativa
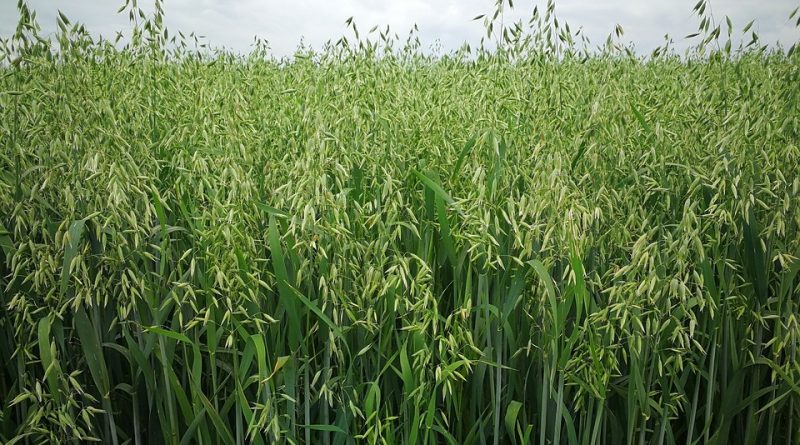
The common oats or simply Avena (Avena sativa L.) is a herbaceous species of the family of poaches (or graminaceous).
Systematics –
From the systematic point of view it belongs to the Domain Eukaryota, Kingdom Plantae, Division Magnoliophyta, Class Liliopsida, Order Poales, Family Poaceae, Subfamily Pooideae, Tribù Aveneae and then to the Genus Avena and to the Species A. sativa.
Etymology –
The term Avena is assonant with the Sanskrit avasa: nourishment, fodder; genre whose name was already used by the Latin Authors, for example by Varro. The specific epithet derives from satum (past participle of sero: sowing, planting) sown, planted: which is sown or planted, cultivated, domestic.
Geographic Distribution and Habitat –
Avena sativa is one of the oldest species cultivated by man, whose area of origin is uncertain because its original provenance is disputed between India, China and Egypt. Today, oats are a widespread crop all over the world, and they are of great importance as equine food in Russia, Poland and Germany.
Description –
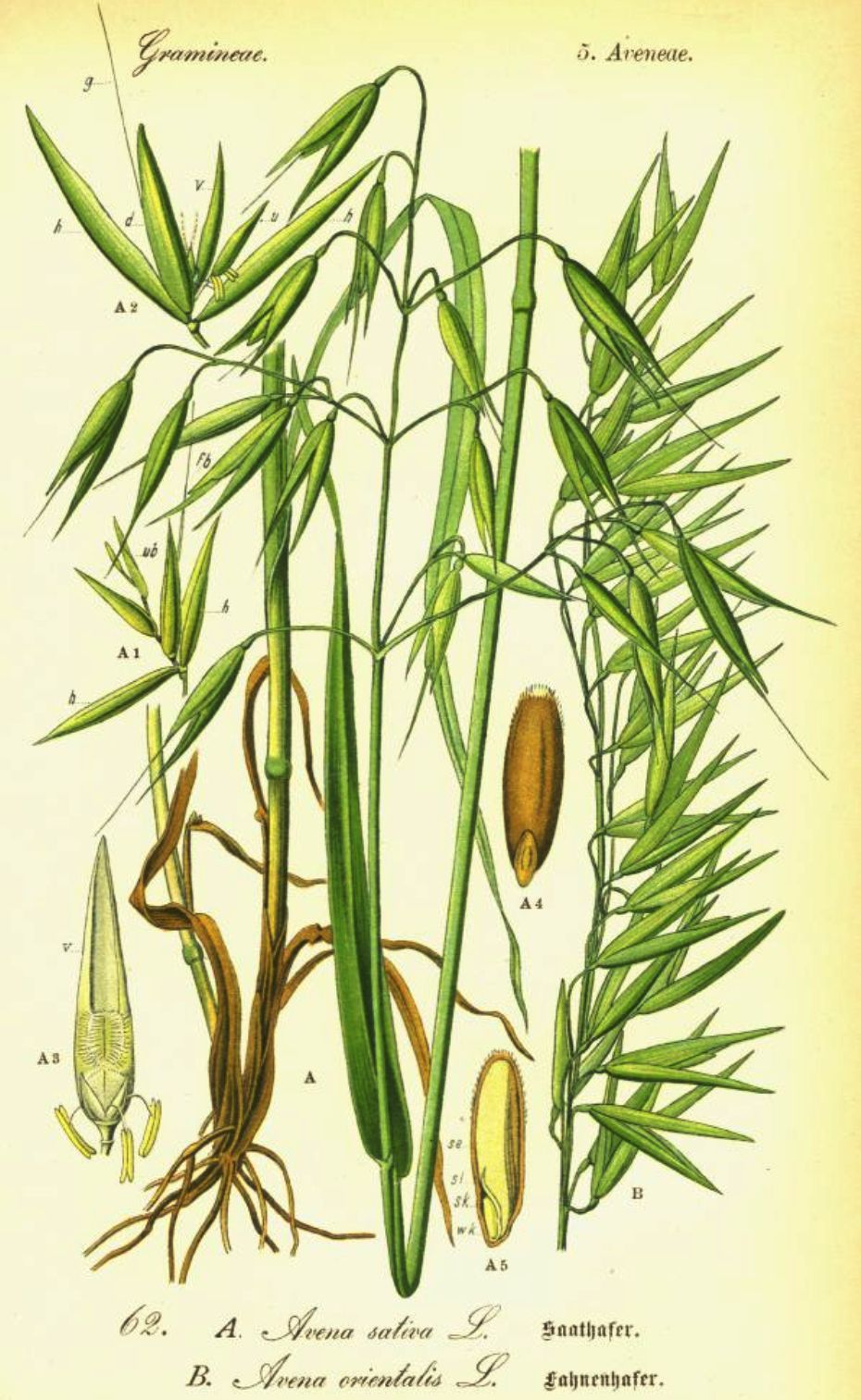
Avena sativa is characterized by the typical grassy stem of the grass (culmo), hollow, thin and divided into several internodes. The leaves are rather thin and elongated with parallel ribs; these are wrapped in sheath around the culm so as to cover each an entire knot.
The flowers are grouped in groups of 2 or 3 in spike-shaped inflorescences; from these the starchy kernels are formed; these are covered with glumette that are prolonged in two subtle arist characteristics.
Cultivation –
The varieties of Avena sativa used in agriculture were selected around 4,500 years ago starting from wild species, from European and Middle Eastern farmers. It is a plant generally sown at the beginning of spring and collected in full or late summer, or, as in the southern regions of Europe and North America, sown also in autumn. In Italy the major productions come from Puglia and Basilicata. For the cultivation technique you can consult the following sheet.
Uses and Traditions –
Oats represent one of the most widely cultivated crops in the world; in fact it is in seventh place in the ranking of the most cultivated cereals. The largest producers of oats in the world are the United States, Russia, Germany, Finland and Poland, being a plant that tolerates well low temperatures. In Italy it is grown today especially in the southern regions where tradition and culture are also obtained biada, a fundamental food for the animals.
There are traces of the consumption of oats since 4000 BC, but it was the wild plant, harvested and consumed mainly in the plains of central Asia and central-northern Europe. The cultivation dates back to the beginning of the Christian Era and spread especially in the northern European regions. In some countries, oats have remained in some countries only a food for animals; this is because it is more difficult to process it, less conservable than other grains and has a higher content of oxidizable fats. In this regard, a sentence by dr. Johnson, who was a famous English scholar, wrote in his Dictionary of 1755: “It is a grain that in England is generally intended for horses, but in Scotland it makes people live”.
For human consumption it is consumed in the form of flakes or very fine flour, which are excellent in infant and elderly nutrition (biscuits, pancakes, etc.). Together with other cereals, Avena sativa enters the preparation of beer and whiskey. This “minor” cereal gives excellent results in cases of depression, nervousness, insomnia and physical or mental exhaustion.
It is an excellent food and supplement for those suffering from stress or sexual impotence; especially students, sportsmen and nursing mothers, find in this plant an ideal food-medicine. It is particularly suitable for convalescents and for those suffering from gastritis, colitis or other digestive disorders, due to its easy digestibility.
Oats are considered the richest cereal of properties since even after processing the germ and the bran, the two parts of the oats that have more nutrients, remain unaltered. Although declining, due to the decrease in livestock, especially horses, in recent years it is cultivated for human nutrition; in fact, oats have become part of our diet also because of its positive effects during low-calorie diets.
Another growing use is that of its extracts for external application, in the form of creams or oils, as emollients for dry, sensitive or irritated skin.
Preparation Mode –
Relegated in the past, especially in some countries, for the feeding of livestock, today the use of oats, especially in recent years, has taken hold in Italy. In other countries, as in England, food is a basic ingredient of the diet. Use in the kitchen of oats varies depending on the shape, whether in flakes, in bran, in grains or flour. In the kitchen, as well as flakes, used in breakfast is used in various soups and in meatballs and patties based on oats.
Guido Bissanti
Sources
– Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia.
– Treben M., 2000. Health from the Pharmacy of the Lord, Advice and experience with medicinal herbs, Ennsthaler Publisher
– Pignatti S., 1982. Flora of Italy, Edagricole, Bologna.
– Conti F., Abbate G., Alessandrini A., Blasi C. (edited by), 2005. An annotated checklist of the Italian vascular flora, Palombi Editore.
Warning: Pharmaceutical applications and alimurgical uses are indicated for informational purposes only and do not in any way represent a medical prescription; there is therefore no liability for their use for curative, aesthetic or food purposes.