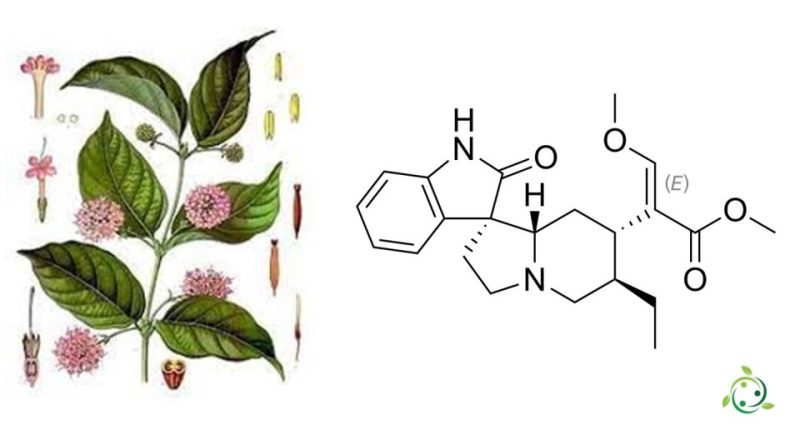
Rhynchophylline
Rhynchophylline
Rinchophylline, whose term in the official IUPAC nomenclature is: Methyl (2E)-2-[(1′R,6′R,7′S,8a′S)-6′-ethyl-2-oxo-1,2 ,2′,3′,6′,7′ ,8′,8a′-octahydro-5′H-spiro[indole-3,1′-indolizin]-7′-yl]-3-methoxyprop-2-enoate , is an alkaloid present in some species of Uncaria (Rubiaceae). It is found in particular in Uncaria rhynchophylla and Uncaria tomentosa.
This alkaloid is also present in the leaves of Mitragyna speciosa, a tree native to Thailand. Chemically, it is related to the alkaloid mitragynine.
Rhinchophylline has the chemical formula: C22H28N2O4.
Rhinchophylline is a non-competitive NMDA antagonist (IC50 = 43.2 μM) and a calcium channel blocker.
This substance has a high biological activity and has been widely used in anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective studies.
Rhinchophylline was found to increase serum SOD activity and down-regulated TLR4 expression in hippocampal tissue of juvenile rats with prolonged seizures, suggesting that rincoloflline may have protective effects on brain damage induced by sustained seizures.
The use of rynchofylline arose on the basis of the medicinal properties of plants of the Uncaria species, which have had a variety of uses in traditional herbal medicine, such as dizziness, convulsions, numbness and hypertension. These uses have been associated with the presence of rynchofylline and have encouraged its research as a candidate drug for various cardiovascular and central nervous system diseases; however, few clinically relevant studies have been conducted.
Warning: The information provided is not medical advice and may not be accurate. The contents are for illustrative purposes only and do not replace medical advice.