Polygalin
Polygalin
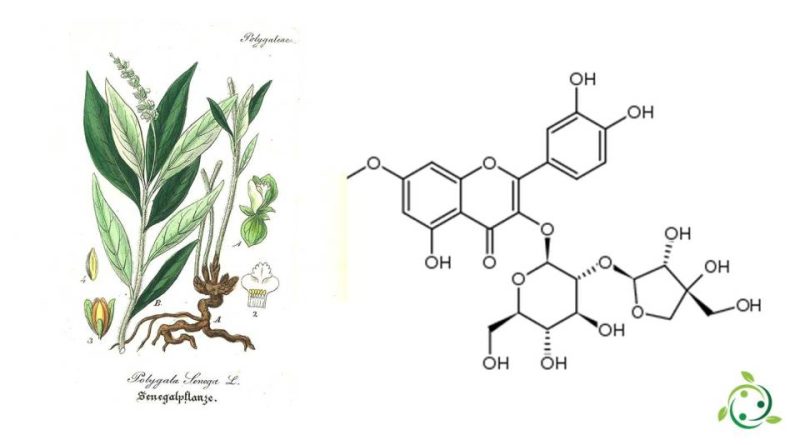
The term polygalin or seneguine refers to a family of compounds of natural origin.
Polygalin is therefore an organic compound and is a saponin (i.e. a terpene glycoside of vegetable origin) previously extracted from a species of polygala (Polygala senega L.) but present in other species of the same genus such as Polygala vulgaris L ..
The chemical formula of these saponins is variable but being glycosides they are always composed of CHO in different proportions depending on the different formula.
One of these polygalin H has formual brute or molecular C30H36O17 and its term in the official IUPAC nomenclature is: 3 – [(2S, 3R, 4S, 5R, 6R) -3 – [(2S, 3R, 4R) -3, 4-dihydroxy-4- (hydroxymethyl) oxolan-2-yl] oxy-4,5-dihydroxy -6- (hydroxymethyl) oxan-2-yl] oxy-2- (3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl) -6- (hydroxymethyl) -5,7-dimethoxicromen-4-one.
Polygalin was extracted above all in the past with a process by distillation of the chopped root of Polygala senega and subsequent drying by evaporation.
It is believed that this substance like other saponins is used by plants as a defensive system against pathogenic organisms, in particular fungi.
In therapy, at the moment, the saponins of some plants are recognized as anti-inflammatory, healing (as in licorice) and anti-edema (as in horse chestnut).
Saponins are often used in industry for the subsequent production of steroid hormones (such as, for example, testosterone and cortisol).
Warning: The information shown is not medical advice and may not be accurate. The contents are for illustrative purposes only and do not replace medical advice.