Scopoletin
Scopoletin
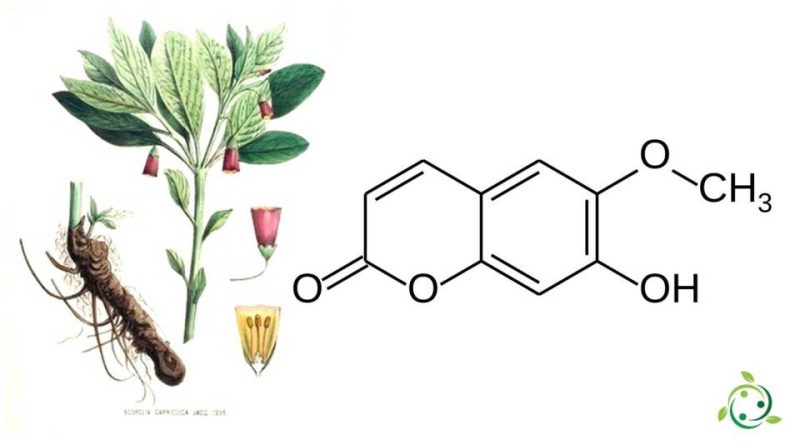
Scopoletin, whose term in the official IUPAC nomenclature is: 7-hydroxy-6-methoxicromen-2-one is a coumarin with a brute or molecular formula: C10H8O4.
Scopoletin is a naturally occurring substance and is found in the root of plants of the genus Scopolia such as (Scopolia carniolica Jacq.) And (Scopolia japonica Maxim.), In chicory, in some plants of the genus Artemisia (Artemisia scoparia Waldst. & Kit. 1802 not Maxim. 1859), in the roots and leaves of the nettle (Urtica dioica L., 1753) and in other plants such as:
– Passiflora incarnata L., 1753;
– Brunfelsia spp. L.;
– Viburnum prunifolium L .;
– Solanum nigrum L. 1753;
– Datura metel L :;
– Mallotus resinosus (Blanco) Merr .;
– Kleinhovia hospita L.
However, scopoletin can also be found in fenugreek, vinegar, some whiskeys or dandelion coffee.
Scopoletin is normally extracted from Japanese nightshade (Scopolia japonica Maxim.).
This substance has analgesic, anti-inflammatory, nootropic, neuroprotective, hypotensive, antioxidant, antidepressant, anxiolytic, antibacterial, antitumor and slimming properties; properties supported by scientific research.
Scopoletin is derived from 1,2-benzopyrone which is the central structure of coumarins formed through hydroxylation of cinnamates, trans / cis isomerization of the side chain and lactonization.
From the point of view scopoletin is highly fluorescent when dissolved in DMSO or water and is regularly used as a fluorometric test for the detection of hydrogen peroxide in combination with horseradish peroxidase. When oxidized, its fluorescence is strongly suppressed.
Warning: The information shown is not medical advice and may not be accurate. The contents are for illustrative purposes only and do not replace medical advice.