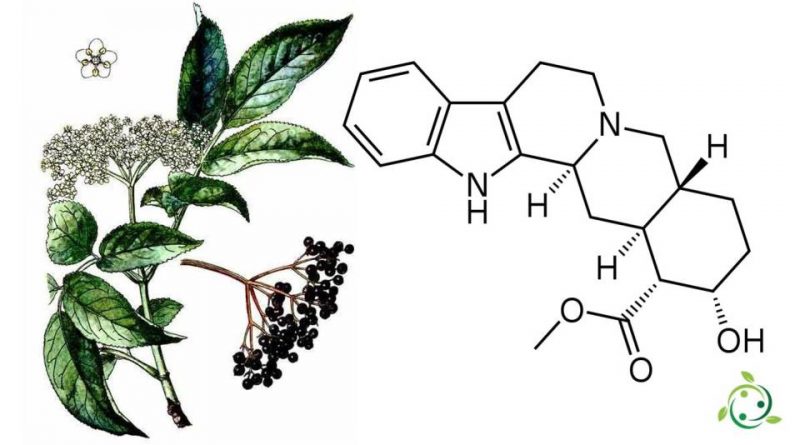
Yohimbine
Yohimbine
Yohimbine, whose term in the official IUPAC nomenclature is: 17α-hydroxy-yohimban-16α-carboxylic acid methyl ester is an alkaloid.
Yohimbine has a brute or molecular formula: C21H26N2O3 and an indole alkaloid with stimulating effects on the central nervous system.
Yohimbine is a substance derived from the bark of the African Johimbe or yohimbe tree (Pausinystalia johimbe (K. Schum.) Pierre ex Beille, 1906).
Yohimbine is an alpha-2 adrenergic antagonist and has been used in a variety of research projects. It is a veterinary drug used to reverse sedation in dogs and deer.
While yohimbine acts as an aphrodisiac in some mammals, it does not in humans. It has been prescribed as a treatment for erectile dysfunction, but its reported clinical benefits have been modest and has largely been replaced by the PDE5 inhibitor class of drugs.
Substances that have been extracted from the yohimbe tree have been marketed as food supplements for various purposes, but they contain highly variable amounts of yohimbine, if any; to date, there is no published scientific evidence that supports their effectiveness.
The compound is also endowed with an antidiuretic effect and produces an increase in heart rate and blood pressure. The molecule has a marked psychoactive action and it has been reported that it can cause altered responses of the central nervous system (CNS), including anxiety and manic reactions. Other effects that could explain its marked psychoactivity and some side effects (although the neurobiological role of the following effects has not yet been fully elucidated) are: agonism at the 5-HT1d and 5-HT2a serotonin receptors and antagonism of 5-HT1b and 5-HT2b.
It has been reported that this molecule could lead to a reduction in body fat but, in this regard, many doubts persist.
Yohimbine has also been studied as a remedy for type 2 diabetes in animal and human models carrying the alpha2-adrenergic receptor subtype “A” gene polymorphism.
Among the side effects and unwanted effects, depending on the dosage taken, yohimbine can also lead to an increase in blood pressure, which is often accompanied by an increase in heart rate. Adverse gastrointestinal symptoms may also occur including nausea and vomiting. Due to its excitatory effects on the CNS, the molecule often arouses irritability, generalized anxiety, excitement, motor hyperactivity, manic reactions, hallucinations, insomnia, tremor and vertigo.
Yohimbine is contraindicated in cases of hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients used in the pharmacological formulation. It is also contraindicated in hepatic and renal insufficiency.
Furthermore, the simultaneous intake of yohimbine and antidepressant drugs or phenothiazines may involve an increased risk of side effects.
Warning: The information shown is not medical advice and may not be accurate. The contents are for illustrative purposes only and do not replace medical advice.