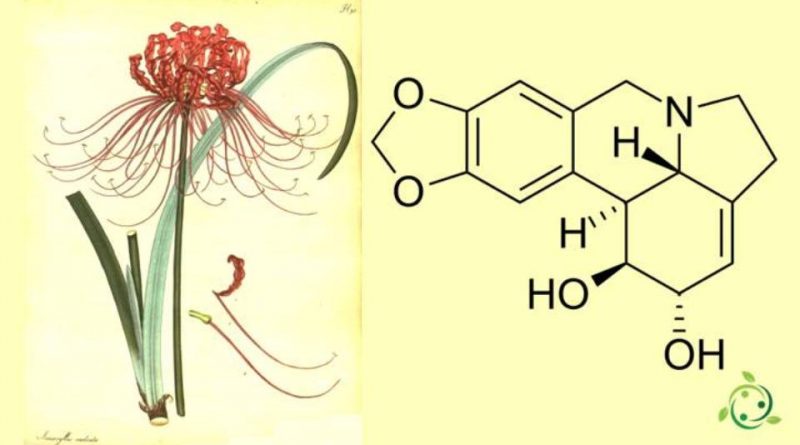
Lycorine
Lycorine
Lycorine, whose term in the official IUPAC nomenclature is: 1,2,4,5,12b, 12c-hexahydro-7H- [1,3] dioxol [4,5-j] pyrrol [3,2,1-de ] phenanthridine-1,2-diol is an alkaloid of natural origin.
Lycorine, also known by the names of galantidine, amaryllis dina or narcissin, has a brute or molecular formula: C16H17NO4.
From the physical point of view it is presented in the form of white, poisonous crystals with an emetic action.
Lycorine is an alkaloid contained in a species of the licoride genus (Lycoris radiata (L’Hér.) Herb.) Which is a bulbous plant of the Amarillidaceae family and in other species.
Lycorine is a toxic compound that in these plants is synthesized in the leaves, but transferred and accumulated in the bulbs.
This alkaloid can be highly poisonous, or even lethal, if ingested in large quantities.
Symptoms of intake poisoning are: vomiting, diarrhea and convulsions.
Lycorine inhibits protein synthesis and can inhibit the biosynthesis of ascorbic acid in plants.
Studies on its inhibitory activities were conducted on this substance in the 1970s, which highlighted a role of lycorine as an inhibitor of the division of cancer cells and an antiviral effect.
Warning: The information shown is not medical advice and may not be accurate. The contents are for illustrative purposes only and do not replace medical advice.