Allantoin
Allantoin
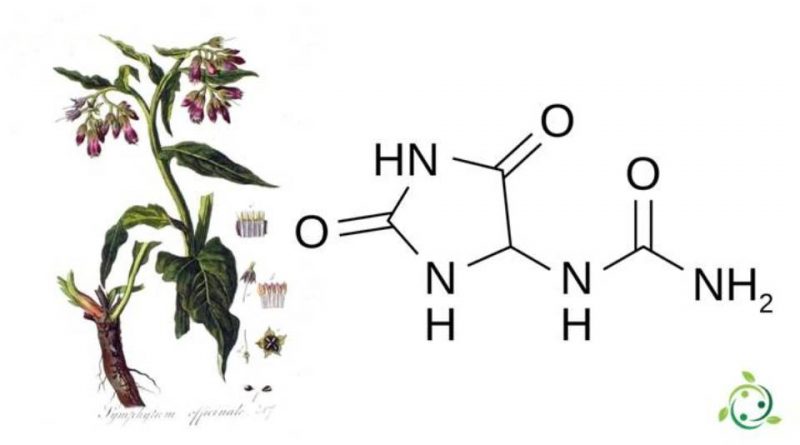
Allantoin whose term in the official IUPAC nomenclature is: (2,5-Dioxy-4-imidazolidinyl) urea is an urea with a brute or molecular formula C4H6N4O3.
Allantoin was discovered by a group of British scientists in the early 1900s. This substance is found in some plants, such as Symphytum officinale, a plant with anti-inflammatory and healing properties, which is also useful against digestive disorders, arthrosis and cramps, in sugar beets, Aloe vera, chamomile and other plants. .
Allantoin is also naturally produced in some mammals.
In fact, allantoin is the final product of the oxidation of uric acid which is catalyzed in vivo by the enzymes urate oxidase and 5-hydroxyurate hydrolase. In addition to some plants it is produced through the metabolic pathway called purine catabolism.
In animals it can be found in the urine of almost all mammals except primates lacking the enzyme urate oxidase. It is normally produced by chemical synthesis with different processes: through oxidation reactions with urea permanganate, or with high temperature reactions of urea in dichloroacetic acid, or by condensation of urea and glyoxylic acid. The synthesis product contains both enantiomers, R and S, in similar concentrations.
The presence in the human species, according to some authors, would further demonstrate the discussed ability of uric acid to act as an antioxidant at normal concentrations in tissues. What its cellular effects are, however, is not known.
According to a study carried out a few years ago, it was found that the appearance of plasma allantoin in patients suffering from chronic coronary heart disease is associated with an unequivocal involvement of oxidative stress. In addition, a posthumous study has shown that its skin concentrations are higher in patients suffering from the autoimmune syndromes vitiligo, Behcet’s disease and rheumatoid arthritis.
This would confirm the original hypothesis of the role of oxygen free radicals in the appearance of skin lesions linked to diseases. In any case, this condition could be caused by oxidative stress that could come from the xanthine / xanthine oxidase axis, that is, from the metabolism of uric acid.
Allantoin today finds numerous applications in medicine and cosmetics. This substance has been recognized by the US (USP, European (European Pharmacopoeia) and British (British Pharmacopoeial Codex) pharmacopoeia as a dermatological and vulnerary agent.
The FDA classifies allantoin as a skin protective substance in OTC products with concentrations between 0.5% and 2%. In cosmetics it is considered keratolytic and re-epithelizing, like urea, although due to its poor solubility in water it is used at relatively low concentrations.
Allantoin is not irritating, but calming and soothing, therefore ideal for skin rashes, redness, irritation or scars. However for cosmetics it is created in the laboratory.
Warning: The information shown is not medical advice and may not be accurate. The contents are for illustrative purposes only and do not replace medical advice.