Bisabolens
Bisabolens
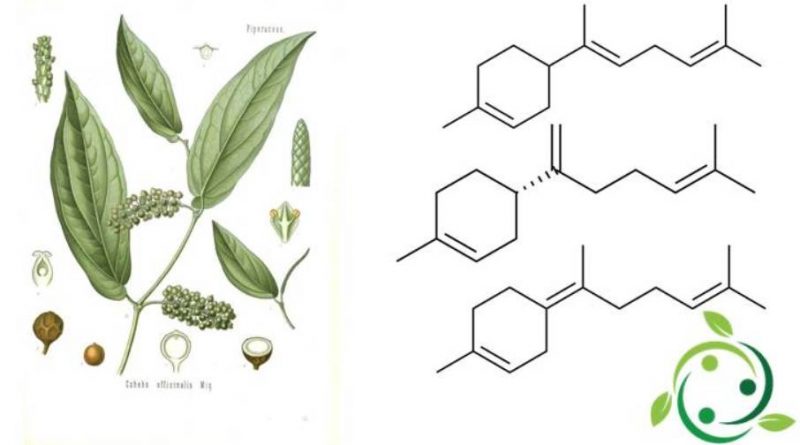
Bisabolens are a group of closely related natural chemical compounds that are classified as sesquiterpenes. Specifically there are three isomers, which differ in the position of the carbon-carbon double bonds, with the configurations α, β and γ which respectively take the names of in the official IUPAC nomenclature:
– (α): (E) -1-Methyl-4- (6-methylpta-2,5-dien-2-yl) cyclohex-1-ene;
– (β): (S) -1-Methyl-4- (6-methylpta-1,5-dien-2-yl) cyclohex-1-ene;
– (γ): (Z) -1-Methyl-4- (6-methylpt-5-en-2-ylidene) cyclohex-1-ene.
Bisabolens have a brute or moleolar chemical formula: C15H24 and are produced from farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) which is an intermediate compound with 15 carbon atoms of the metabolic pathway of mevalonic acid, used by living organisms in the biosynthesis of terpenes, terpenoids and sterols.
Bisabolens are therefore naturally occurring compounds in the essential oils of a large variety of plants.
These compounds are present, among other plant species, in angelica (Angelica archangelica L.), ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe, 1807) but also in cubebe, lemon and oregano.
Many bisabolene derivatives also act as pheromones in various insects, such as bedbugs and fruit flies, moreover these compounds are produced by different mushrooms, even if their biological role at the moment remains unclear.
Furthermore, bisabolens are intermediate in the biosynthesis of many other natural chemical compounds, including Ernandulcin, a natural sweetener.
Β-bisabolene has a balsamic odor and is approved in Europe as a food additive.
Warning: The information shown is not medical advice and may not be accurate. The contents are for illustrative purposes only and do not replace medical advice.