Niacin
Niacin
The term niacin means two similar molecules: nicotinic acid (niacin proper) and the amide of the latter, nicotinamide (or niacinamide).
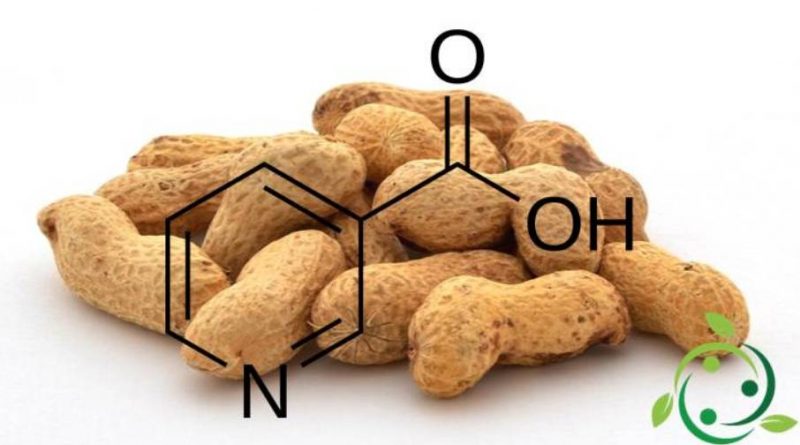
The IUPAC name of this molecule is: pyridin-3-carboxylic acid while the common names are nicotinic acid and vitamin B3. Niacin has a brute or molecular formula: C6NH5O2. From a physical point of view, niacin is one of the most stable vitamins as it does not easily oxidize in contact with oxygen, heat and light.
It is present in many plants, in more or less high amounts and particularly in peanuts and cereals; it is also present in many foods including: white and red meat, tuna, salmon, milk and cheese. Unlike other vitamins, this substance is only contained in low quantities in eggs, fruit and vegetables. But whole grains, bran, milk and cheese are rich. Niacin can be taken through supplements, in cases where the diet can not provide enough. Niacin is part of the vitamin B complex together with Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) and Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin).
It is also called vitamin PP (“pellagra preventive factor”) for its effective action against pellagra: the disease once widespread among the populations that used only polenta or corn and caused precisely by the vitamin B3 deficiency.
Niacin is a water-soluble vitamin that performs many functions on the human saddle. Its presence, under optimal conditions improves the level of cholesterol in the blood, keeps the skin healthy and helps fight acne, protects against Alzheimer’s and other age-related brain diseases; it is also a help against impotence.
Niacin or vitamin B3 is a necessary substance for the processes that imply cellular respiration, it also helps in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins, promotes good circulation and skin health, helps the functioning of the nervous system and the normal secretion of bile and stomach fluids. Niacin enhances memory and also appears to be effective in treating anxiety. It is also useful in improving circulation and reducing blood cholesterol levels. In this regard, niacin at high doses (and generally in combination with statins) can increase levels of good cholesterol (Hdl) and lower triglycerides, in the same way as some medicines. Because of these properties, vitamin B3 has benefits for heart health, including the ability to reduce atherosclerosis.
In general, niacin is a well-tolerated substance, but it also has some side effects.
As with any substance, overdoses can cause side effects. The most common are headaches, lowering of pressure, dizziness and dizziness. Before taking the substance through supplements or ad hoc drugs, it is best to ask your doctor. The indication is especially valid for those who are in drug therapy for some disorder.
Warning: The information reported is not medical advice and may not be accurate. The contents are for illustrative purposes only and do not replace medical advice.