Mannitol
Mannitol
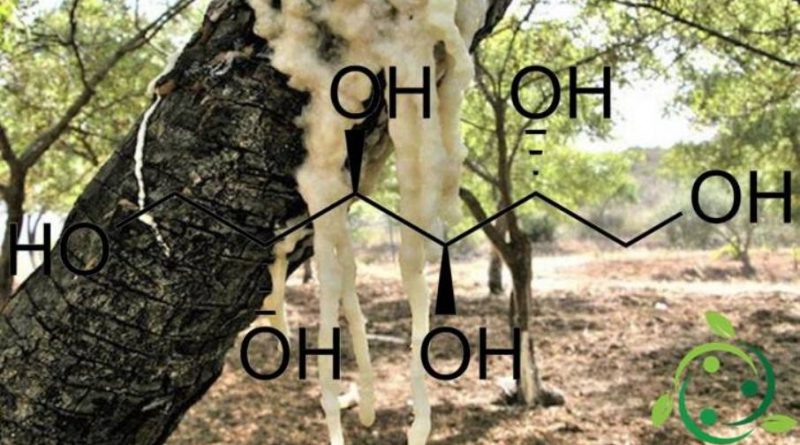
Mannitol, whose name in the IUPAC nomenclature is: (2R, 3R, 4R, 5R) esan 1,2,3,4,5,6 esol, has the brute or molecular formula, C6H14O6.
Mannitol (or D – (-) – mannitol, or E421), often also called mannite, is a chiral alditol, with six hydroxyl groups at the aliphatic chain consisting of six carbon saturated atoms. It is a simple carbohydrate belonging to the category of hexahydic polyalcohols.
Mannitol is a very common carbohydrate in the plant world. It is found in very significant concentrations in the ash manna (30-60%), in the laminaria and fucus (marine algae), in the leaves and in the drupes of the olive tree, in the fig tree, in the celery and in edible mushrooms like Lactarius spp. ., Agaricus spp. and other species. At an industrial level, mannitol is produced from sucrose.
This compound, at room temperature, is presented as an odorless white solid. Mannitol is widely used in the pharmaceutical sector for its diuretic properties; in particular, it belongs to the class of osmotic diuretics. Also in the food field it is widely used and belongs to the category of stabilizers, thickeners, gelling agents and emulsifiers. In reality it is used above all as a sweetener.
As for its use as a drug, it exerts an osmotic imbalance in the lumen where it is placed (digestive tract or in the kidney following injection) acting as a diuretic (forms a hypertonic solution and invokes water by osmosis within the renal tubules, or water and mineral salts within the digestive tract). It is mainly used in situations of intoxication where it is necessary to eliminate in a short time a toxic substance (unless it is an acid or a strong base, a condition that prohibits the use of mannitol) or in acute conditions with severe edema, such as example of cerebral edema.
In the past it was also used as a laxative in pediatrics, adding them in small doses dissolved in warm milk.
In use as a sweetener it is not very widespread as it is an energy sweetener. In fact it has a sweetening power slightly higher than half of that of sucrose and has a caloric power that is higher than half of that of sucrose itself. In practice, nothing is gained as a relationship between sweetening power and calories by using mannitol instead of normal sugar.
Furthermore, the use of mannitol must be carried out with particular precaution. In case of excess of mannitol intake the main disorders are gastrointestinal (laxative effect), which is why in some countries, as in Australia, its use in baby food is prohibited.
To avoid such effects, therefore, the acceptable daily dose is 50 mg / kg of weight, even if, regardless of the side effects, it is not a dangerous compound for health, being a carbohydrate in effect, easily metabolized by our body. In its pharmaceutical use, taken intravenously (in cases of chronic renal failure, intracranial hypertension, spinal and cerebral masses, intraocular hypertension, for the renal elimination of toxic substances and for the measurement of glomerular filtrate) the allowable dose varies between 50 and 200 g per day.
Warning: The information reported is not medical advice and may not be accurate. The contents are for illustrative purposes only and do not replace medical advice.