Terpinolene
Terpinolene
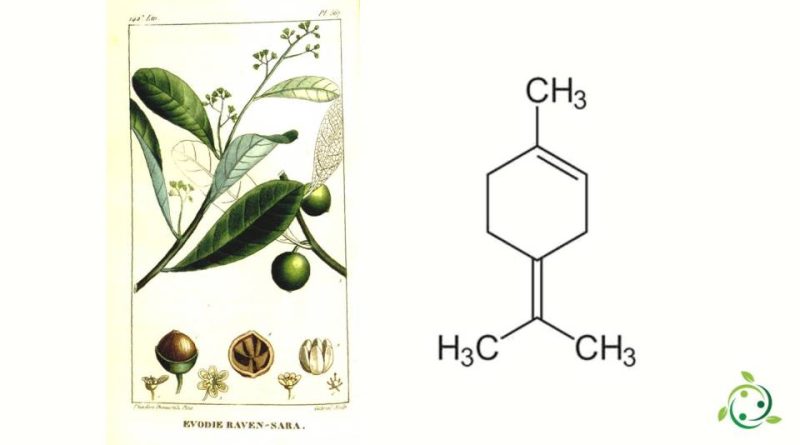
Terpinolene, whose term in the official IUPAC nomenclature is: 1-methyl-4-propan-2-ylidenecyclohexene, is a p-mentadiene with double bonds in positions 1 and 4.
Being a monoterpene it is a small and simple molecule as two isoprene units define its molecular structure placing it in this category, alongside terpenes such as limonene and myrcene.
Terpinolene has the brute or molecular formula: C10H16 and, from a physical point of view, it is presented as a water-white to light amber colored liquid. It is insoluble in water and is less dense than water.
Occurrence in nature –
Terpinolene is found in various plants, being part of the composition of many essential oils, such as in: Citrus, Mentha, Juniperus, Myristica. Furthermore, the Pastinaca sativa plant is an important source of this terpene but it is found in many other plants, such as in the Ravensara aromatica and in its essential oil, and it is contained, in different concentrations, in the narrow leaf leaves of the tea, celery, Scots pine, nutmeg, marjoram, valerian, oregano, coriander, rosemary, basil, sage and ginger.
Finally, terpinolene is one of over 200 terpenes produced by the cannabis plant. This molecule is present in many of the more modern chemotypes of cannabis, albeit in relatively small quantities compared to other members of the same chemical class. Researchers have found that this terpene is mostly found in sativa strains.
Despite its low concentrations, terpinolene manages to contribute significantly to the overall aroma of many cannabis strains (demonstrating clear aromatic intensity).
The presence of this molecule in cannabis and other plants, together with a myriad of other terpenes and cannabinoids, is linked to the action that these plants activate to defend themselves against harmful insects and fungal pathogens, thanks to the larvicidal and antifungal properties of the molecule.
Property –
Terpinolene is a flavoring ingredient and has been shown to have an antifungal function (A7932).
It plays a role as a sedative, insect repellent, plant metabolite and volatile oil component.
Terpinolene releases an aroma reminiscent of the smell of the woods, recalling the refreshing aromas of the earth, where hints of pine, wood, flowers, herbs and delicate citrus notes are appreciated.
Furthermore, like many of the components present in the cannabis plant it shows some interesting therapeutic effects, although scientific research has yet to verify its full potential.
In any case, if the researches find further confirmations, its most promising properties are:
– Anticancer;
– Antioxidant;
– Analgesic;
– Anti-inflammatory;
– Possible sedative;
– May protect against cardiovascular disease.
Among other things, several studies have demonstrated the anticancer potential of terpinolene. The molecule appears to alter the signaling pathways that induce the survival and growth of cancer cells. Research published in the journal Oncology Letters documents how terpinolene can actually produce these effects.
The study found that the terpene was effective in reducing the expression of protein kinase B (also known as AKT), which often contributes to cancer progression through mediation of cell proliferation and survival signals. Thus, increased AKT expression is thought to be implicated in numerous types of human cancers.
As regards the sedative properties, it is not yet clear how and if this molecule produces these effects. However research has so far found that a low dose of 0.1mg can reduce motor activity by 67.8%. Should future human studies show similar results, terpinolene could play a beneficial role in health issues such as anxiety and insomnia.
Finally, promising data would lead us to think that terpinolene could also help protect against certain cardiovascular disorders.
Uses –
Terpinolene is an organic compound of natural origin that can play an important role as a starting substance for other compounds.
Due to its aromatic properties, it represents, above all, a starting substance for making products such as soaps and perfumes.
Furthermore, beyond its properties in the field of medicine, which have yet to find confirmation and verification, it can be used to produce plastic materials and resins.
Warning: The information provided is not medical advice and may not be accurate. The contents are for illustrative purposes only and do not replace medical advice.