Gramine
Gramine
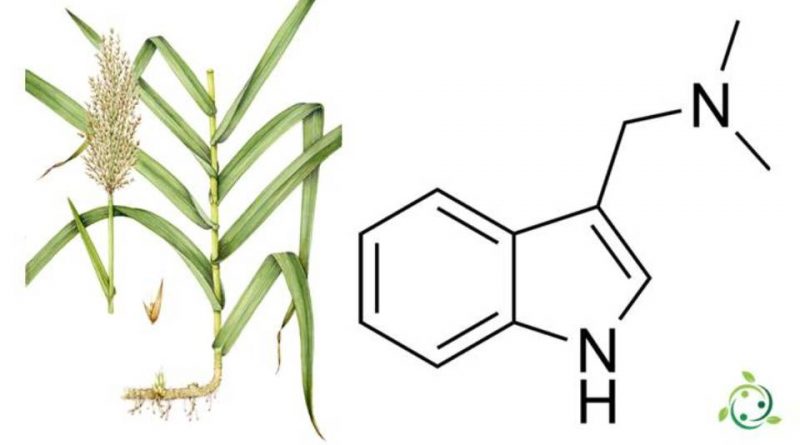
Gramine, whose term in the official IUPAC nomenclature is: N, N-dimethyl-1H-indole-3-methanamine or 3- (dimethylaminomethyl) indole, is an alacloid.
Gramine has a brute or molecular formula: C11H14N2 and is an indole alkaloid of natural origin, present in numerous plants, in particular poaceae.
This alkaloid has been isolated in plants of the genus Phalaris and in particular: Phalaris aquatica L., Phalaris arundinacea L. and Arundo donax L.
Research on gramina suggests its important role in the defense against parasites as it is toxic for many organisms.
Among other things, it is believed that gramina is one of the molecules responsible for the lack of palatability in some herbivores given its similarity to skatole (3-methylindole), responsible for the bad odor of feces.
In the laboratory the gram was administered to guinea pigs; This resulted in kidney injury, poor weight growth and death (with 0.25% and 0.5% referring to the complete diet), although no symptoms directly related to the nervous system were observed.
Gramine is also used in organic chemistry for the synthesis of tryptophan.
Warning: The information is not medical advice and may not be accurate. The contents are for illustrative purposes only and do not replace medical advice.