Boldine
Boldine
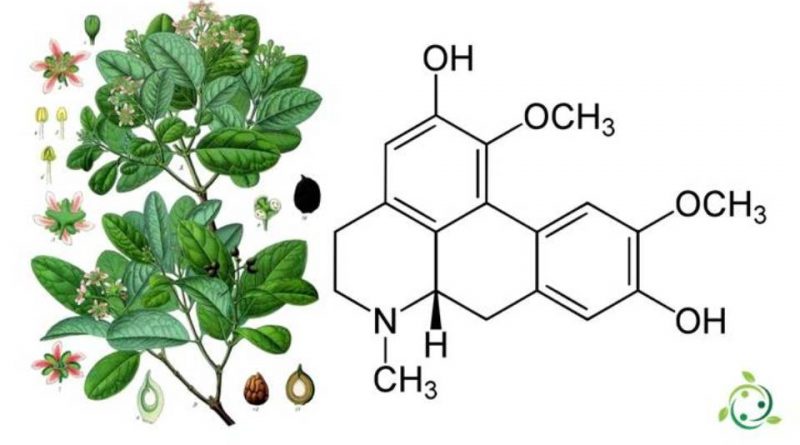
Boldine is an alkaloid whose term in the official IUPAC nomenclature is: (8S) -1,13-dimethoxy-7-methyl-5,6,6a, 7-tetrahydro-4H-dibenzo [de, g] quinolin-2, 12-diol.
Boldine has brute or molecular formula: C19H21NO4.
This alkaloid is extracted in nature from some plants, such as from the leaves of the boldo (Peumus boldus Molina) which is an evergreen plant originating from Argentina, Chile and Peru and is also present in the Lindera aggregata (Lindera aggregata (Sims) Kosterm. ).
Boldine appears as a white powder, if pure, bitter, with choleretic and colagogue action.
Among the properties of this alkaloid it is highlighted that pure crystallized boldin causes an increase in biliary secretion that is five times higher than the volume secreted normally. It also exerts an intense hypotensive action in the vagotomized dog.
In the past, the boldo plant extracts were used as choleretics; it still finds limited use in oral preparations with laxative action, in association with other drugs and is the subject of studies for its antioxidant properties.
Boldine has an antioxidant activity that effectively protects against lipid peroxidation induced by free radicals or enzymatic inactivation. Furthermore, it has alpha-adrenergic antagonistic activity in vascular tissue and has also been reported for hepatoprotective, cytoprotective, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effects.
It also exhibits anti-inflammatory activity as it reduces TNF-α expression in Ab-induced chronic inflammation in APP / PSI mice.
Boldine also exhibits neuroprotective effects due to its ability to cross the blood brain barrier (BBB) when administered orally.
Warning: The information given is not medical advice and may not be accurate. The contents are for illustrative purposes only and do not replace medical advice.