Bergamotene
Bergamotene
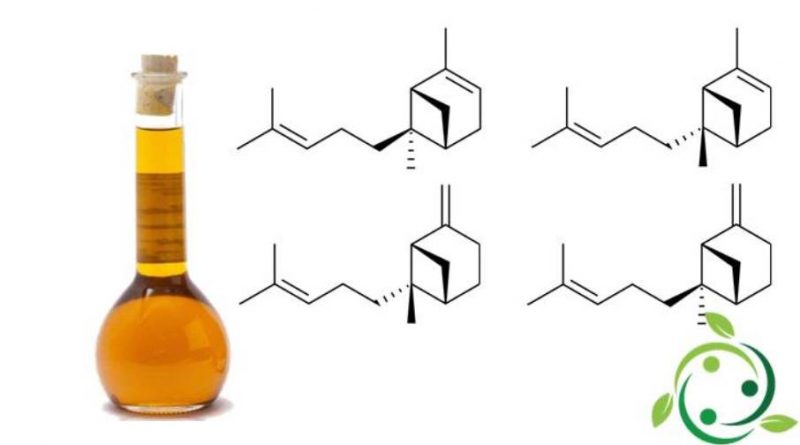
Bergamotenes are a group of chemical compounds with a brute or molecular formula: C15H24.
Of these compounds there are two structural isomers, which are: α-bergamotene and β-bergamotene, which differ only in the position of a double bond.
Their term in the IUPAC official nomenclature is:
– (α): 2,6-dimethyl-6- (4-methylpent-3-enyl) bicycle [3.1.1] ept-2-ene;
– (β): 6-methyl-2-methylidene-6- (4-methylpent-3-en-1-yl) bicycle [3.1.1] heptane.
Both these isomers have, in turn, stereoisomers, the most common of which take the prefix cis and trans.
In nature, bergamotenes are found in numerous plants, and in particular in their essential oils.
Α-Bergamotene is found in carrot, bergamot, lime, cedar, cotton seed, kumquat, basil, etc. oils.
Bergamotenes also have another peculiarity: for some insects they are pheromones.
For example, β- trans-bergamotene is a pheromone for the Melittobia digitata wasp.
In their evolution, plants have developed forms of defense against attacks by herbivorous insects by producing pheromones such as bergamotenes that attract predators of herbivorous insects.
In a more complex mechanism, a species of tobacco, Nicotiana attenuata (Nicotiana attenuata Torr. Ex S.Watson) emits α- trans-bhamamotene from its flowers at night to attract a moth the moth: the sphinx of tobacco tobacco hawk ( Manduca sexta Linnaeus, 1763) as a pollinator; however, during the day the leaves produce α-trans-bhamamotene to attract predatory insects to feed on larvae and eggs that the pollinator may have produced.
Warning: The information shown is not medical advice and may not be accurate. The contents are for illustrative purposes only and do not replace medical advice.