Helenalin
Helenalin
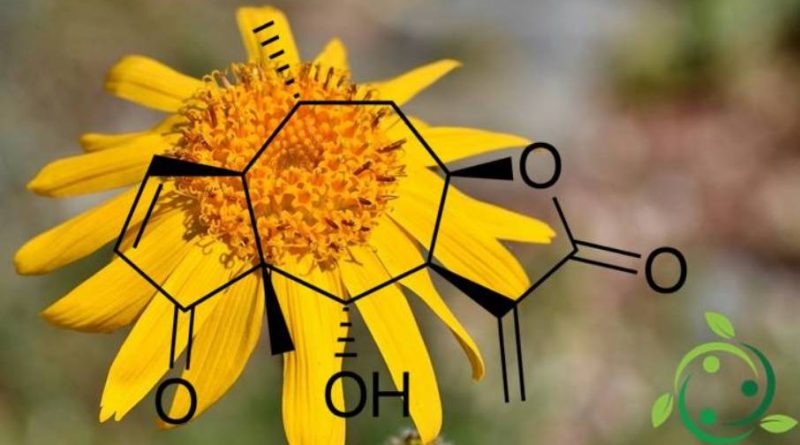
Helenalin, whose term in the official IUPAC nomenclature is: o (-) – 4-hydroxy-4a, 8-dimethyl-3,3a, 4a, 7a, 8,9,9a-octahydroazulen [6,5-b] furan-2,5-dione, and whose molecular brute formula is: C15H18O4 is a sesquiterpene lactone found naturally in Arnica plants (Arnica montana L. and Arnica chamissonis var. foliosa (Nuttall) Maguire). Helenalin is a highly toxic compound and above all hepatic and lymphatic tissues are somewhat vulnerable to its effects. The ingestion of a sufficient amount of helenalin, by ingestion, produces serious gastrointestinal effects and internal bleeding of the digestive tract.
Although toxic, helenalin has some in vitro effects, including anti-inflammatory and anticancer activities. Helenalin can inhibit certain enzymes, such as 5-lipoxygenase and leukotriene C4 synthase. For this reason the compound or its derivatives can find potential medical applications.
Currently there is no in vivo evidence of the anti-inflammatory and anticancer effects of helenalin.
In the past, plant extracts containing helenalin were used as phytotherapy for various treatments, such as blood clotting, muscle tension and rheumatic disorders.
When applied locally to humans, helenalin can cause contact dermatitis in sensitive individuals. However, it is generally considered safe when applied in this way.
The toxicity of helenalin was studied in some mammals such as mice, rats, rabbits and sheep, where the oral LD 50 was established between 85 and 150 mg / kg.
Animal and in vitro studies have also suggested that helenalin can reduce the growth of Staphylococcus aureus and reduce the severity of S. aureus infection.
Warning: The information given is not medical advice and may not be accurate. The contents are for illustrative purposes only and do not replace medical advice.
[:es]