The asparagine
The asparagine
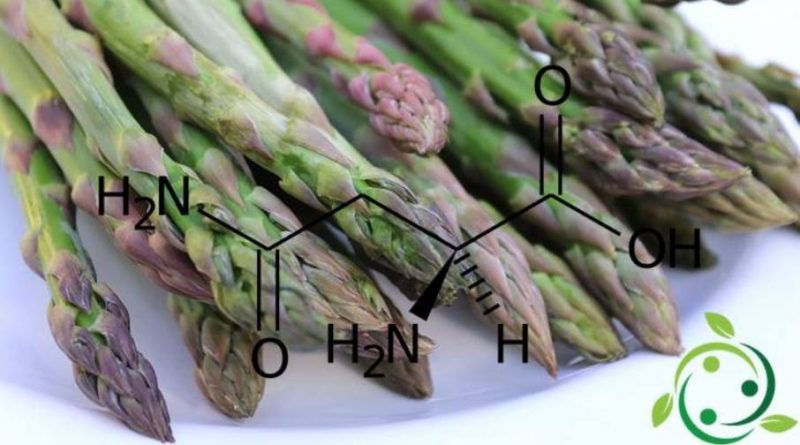
Asparagin is a non-essential, chiral polar amino acid and is the amide of aspartic acid. Enantiomer L is one of the 20 ordinary amino acids that enter the protein constitution. The name asparagine comes from the fact that it was isolated for the first time from asparagus extracts. The diuretic properties of asparagus derive in part from the ability of asparagine to irritate the renal epithelium. Originally it was thought that the typical smell of urine, of those who ate asparagus, was due to some of its metabolites. Later it was understood that in addition to the notable production of N-methylurea, the phenomenon is also due to some sulfur compounds contained by the asparagus.
Asparagine is present in larger doses in some plants; for example in the outer part of coffee, in asparagus shoots and also in potatoes (but also in poultry, seafood and other common foods).
Asparagin in the free form is necessary for the formation of acrylamide, a volatile toxic substance that is produced in increasing quantities with temperature and cooking times. The formation of acrylamide with steam cooking is not known.
Another feature linked to asparagine is that it is actively captured by the cells of some tumors, which use it for cell replication. In the past, the enzyme asparaginase of bacterial origin, was one of the drugs used in the palliative care of some leukemia. This enzyme degraded the asparagine into aspartic acid and ammonium ions; in this way he deprived the leukemic cells of their essential nutrient.
Another use of asparagine is that for the treatment of after-drinking. This molecule is indeed necessary for the metabolism of alcohol. Moreover, aspargina, together with glutamine and creatine, can be found among the preparations that are administered in case of organic asthenia or during long convalescences.
The scientific journal Nature recently published a study that was conducted by oncologists. The study showed that asparagine, in cases of people suffering from breast cancer, promotes the spread of metastases. The experimentation was also carried out by blocking the activity of this substance, or drastically reducing its consumption; it has been found that the number of secondary tumors in the rodents has dropped dramatically: the spread of malignant cells to the bones, the brain and the lungs is one of the main causes of death in patients with this type of cancer.
Warning: The information reported is not medical advice and may not be accurate. The contents are for illustrative purposes only and do not replace medical advice.