Carvone
Carvone
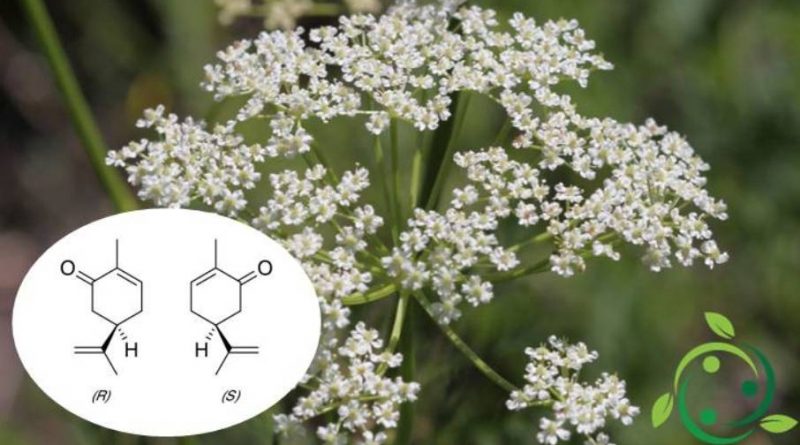
The carvone whose term in the official IUPAC nomenclature is: (R) -5-Isopropenyl-2-methyl-2-cyclohexenone has a brute or molecular formula: C10H14O.
Carvone, from the point of view of chemical classification, is a terpenoid with a boiling point of 231 ° C.
This molecule is soluble in alcohol and chloroform and is composed of two enantiomers both present in nature; it is found in fact, especially in the oil of the caraway seeds (Carum carvi), of the green mentastro (Mentha spicata) and of the dill.
In nature, S – (+) – carvone is the main constituent (60-70%) of cumin seed oil (Carum carvi). It is however present around 40-60% in dill seed oil (Anethum graveolens), and also in orange peel oil.
R – (-) – carvone is instead the predominant component of the essential oil of different mint species, in particular mint oil (Mentha spicata), around 50-80% of R – (-) – carvone .
Even if mint is an excellent natural source of this compound, most of R – (-) – carvone present on the market is synthesized starting from R – (+) – limonene.
R – (-) – Carvone is also found in kuromoji oil (Lindera Umbellata). Some oils, such as the oil of the ginger plant, contain a mixture of both enantiomers.
Many other natural oils, such as peppermint oil, contain traces of carvones.
However both carvones are used in the food industry as aromas. R – (-) – Carvone is also used as an essence to refresh the air and, like many essential oils, carvone containing oils are used in aromatherapy and alternative medicine.
Due to its peculiarities it is used for the creation of aromas and aromas.
Olfactory receptors perceive the two enantiomers differently. R – (-) – carvone, which smells like mint leaves, while S – (+) – carvone, which emits a typical smell of cumin seeds.
The peculiarities of the carvone, although not known as such, have been exploited by the natichita through the caraway plant.
This species was used for medicinal purposes by the ancient Romans.
Only in 1849, by Franz Varrentrapp (1815-1877), was the carvone isolated as a pure compound.
In addition to the aforementioned peculiarities of the carvone, this molecule is used in many fields and applications.
In fact, being this molecule responsible for the scent of cumin, dill and mint, it has been used for thousands of years to give particular aroma to foods.
Furthermore, in agriculture, S – (+) – Carvone is used to prevent the sprouting of potatoes during the storage period.
The other enantiometer, the (R) – (-) – Carvone, after some research, would demonstrate repellent activity against mosquitoes.
Warning: The information given is not medical advice and may not be accurate. The contents are for illustrative purposes only and do not replace medical advice.