4-hydroxybenzoic acid
4-hydroxybenzoic acid
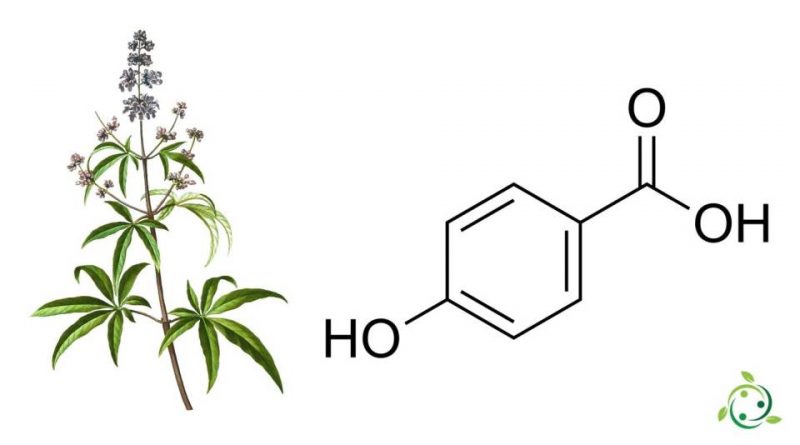
4-hydroxybenzoic acid, known by the abbreviations of 4-HBA or PHBA or with the alternative names of para hydroxybenzoic acid or p-hydroxybenzoic acid, is an organic acid with a brute or molecular formula: C7H6O3.
It is a monohydroxybenzoic acid whose structure consists of a benzene ring with a carboxylic group (-COOH), as in benzoic acid, and a hydroxyl group (-OH) as a substituent in position 4 of the benzene ring.
From a physical point of view, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid is a white crystalline solid slightly soluble in water and chloroform but more soluble in polar organic solvents such as alcohol, ether and acetone.
This substance has an aromatic note of hazelnut and phenol; by the JECFA and the EU regulation it is classified as flavoring in the food sector.
4-hydroxybenzoic acid or its esters and glucosides are present in many living species belonging to different families and genera: from bacteria to algae, from fungi to man. In humans, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid is involved in the biosynthesis of ubiquinone.
4-hydroxybenzoic acid is widely used in organic synthesis, especially its esters, including methyl 4-hydroxybenzoate (paraben Kap), ethyl (ethyl paraben), propyl, butyl, isopropyl, isobutyl, are used as food additives, in the sauce of soy, vinegar, beverages, fruit flavors, fruits and vegetables, pickles, etc; moreover it is also widely used in food, cosmetics, anti-corrosion pharmaceuticals, mold and fungicides, etc.
4-hydroxybenzoic acid, like other parabens, is also used as a base for dyes, pesticides and intermediate products.
4-hydroxybenzoic acid is used in the preservative industry and as a fungicide. It is able to inhibit the growth of mold and is an excellent preservative.
4-hydroxybenzoic acid is a naturally occurring substance isolated from the roots and aerial parts of many plants; for example: Vitex agnus-castus, Vitex negundo, Vitis vinifera, Hypericum perforatum, Daucus carota, Elaeis guineensis, Euterpe oleracea, Fagara macrophylla, Xanthophyllum rubescens, Paratecoma peroba, Tabebuia impetiginosa, Pterocusarponea bantalious santalio Mespilus germanica, Arabidopsis thaliana, Phyllanthus acidus, Macrotyloma uniflorum.
It is also found in various algae such as: Spongiochloris spongiosa, Anacystis nidulans, Sargassum tenerrimum, Sargassum ilicifolium, Sargassum cinereum.
It is also supposed to be one of the active components of a mushroom that has had a medicinal use for a long time: Ganoderma lucidum.
It has also been isolated in many fungi of various genera: Agaricus, Boletus, Cantharellus, Clitocybe, Laccaria, Lactarius, Pleurotus, Russula, Suillus, Termitomyces, etc.
Furthermore, the metabolism of various bacteria involves the production of 4-HBA: Cryptanaerobacter phenolicus, Clostridium hydroxybenzoicum, Sporotomaculum hydroxybenzoicum.
The great diffusion in nature of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, as well as the massive use of its esters in cosmetics, have produced the need to define its exposure levels in humans.
The massive use of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid in the production of cosmetic preservatives or food additives is partly due to its very low acute toxicity: LD 50 is 2200 mg / kg in mice (oral).
As a precursor, but also as a metabolite, of parabens it has been investigated for a suspected estrogenic activity. A valid and reliable study with repeated administration of oral dosages up to 1000 mg / kg body weight using rats (42 days) and valid and reliable studies in immature female rats and mice with repeated administration of dosages up to 100 mg / kg weight body for 3 consecutive days (uterotrophic assays) were available and mainly used for evaluation.
The repeated dose toxicity study in rats (Nagao et al., 1997) did not indicate any effect on the reproductive organs of female and male rats or / and functional aspects of fertility by p-hydroxybenzoic acid. Reliable uterotrophic tests (Twomey 2000b, Hossaini et al. 2000) were negative for p-hydroxyenzoic acid in rats and mice in concentrations up to 100 mg / kg body weight.
In summary, there are a sufficient number of sufficiently reliable and valid studies to evaluate the possible estrogenic effects of p-hydroxybenzoic acid. To date, none of these studies have shown an estrogenic effect of p-hydroxybenzoic acid.
Warning: The information shown is not medical advice and may not be accurate. The contents are for illustrative purposes only and do not replace medical advice.