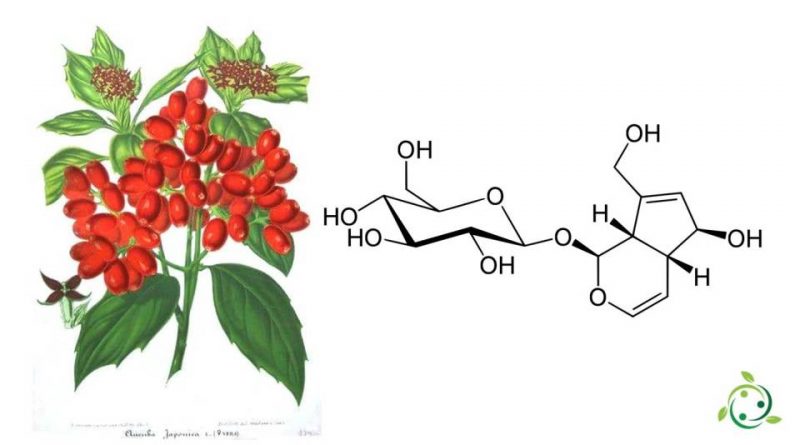
Aucubin
Aucubin
Aucubin, whose term in the official IUPAC nomenclature is: (1S, 4aR, 5S, 7aS) -5-hydroxy-7- (hydroxymethyl) -1,4a, 5,7a-tetrahydrocyclopenta [c] pyran-1-yl β-D-glucopyranoside is an iridoid glycoside with brute or molecular formula: C15H22O9.
Aucubin is an iridoid glycoside that occurs naturally in some plants such as the leaves of Aucuba japonica (Cornaceae), Eucommia ulmoides (Eucommiaceae), and Plantago asiatica, Plantago major, Plantago lanceolata (Plantaginaceae), Galium aparine (Rubiaceae) and still others.
Aucubin, like other iridoid glycosides, plays the role of a defense compound in plants and reduces the growth rates of many generalist herbivores.
Aucubin was found to protect against liver damage induced by carbon tetrachloride or alpha-amanitin in mice and rats when 80 mg / kg were administered intraperitoneally.
Aucubin is also an aperiente (a mild purgative drug) and stimulates the secretion of uric acid by the kidneys.
The biosynthesis of aucubin sees geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP) as a precursor of iridoids. Geranyl phosphate is generated via the mevalonate pathway or the methyleritritol phosphate pathway.
Warning: The information shown is not medical advice and may not be accurate. The contents are for illustrative purposes only and do not replace medical advice.